The National Institute of Health (NIH) defines a clinical trial as:
“A research study in which one or more human subjects are prospectively assigned to one or more interventions (which may include placebo or other control) to evaluate the effects of those interventions on health-related biomedical or behavioural outcomes.”
Many different types of clinical trials exist:
- Phase 0-IV
- Descriptive vs analytical
- Observational/non-experimental or epidemiological vs experimental
- Retrospective, cross-sectional, prospective or ambidirectional
- Recruitment based on cause (cohort) or consequence (case-control)
Clinical trials are a crucial part of the development of a new medicine as they provide the regulatory agencies with the necessary information to weigh the benefits and risks of the new product. Therefore, as shown in this figure, they are a bottleneck in the development process of new potential medicines.
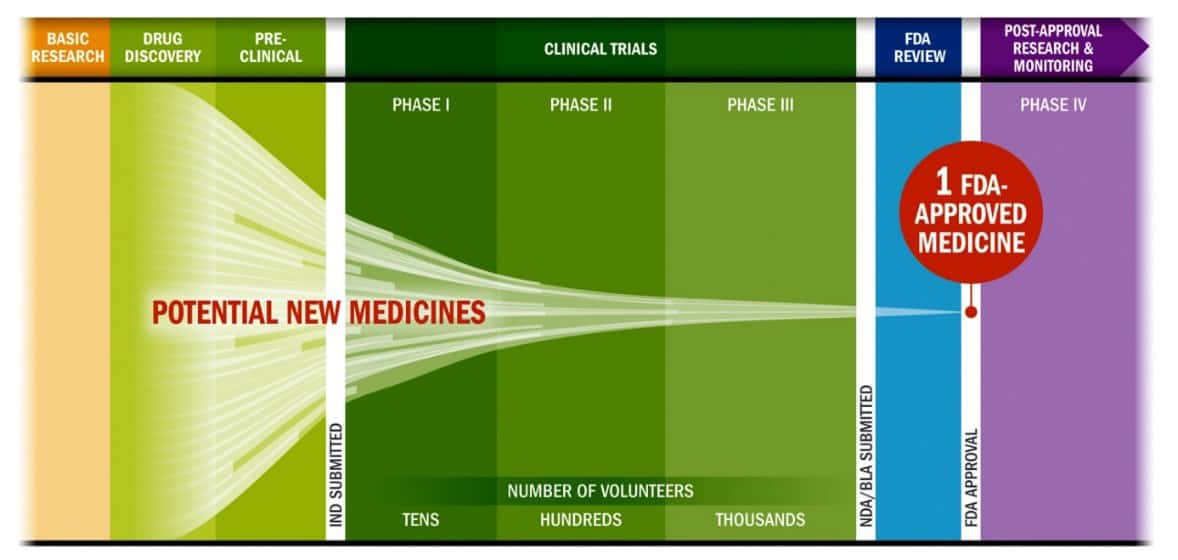
An overview of the development timeline of a new medicine.
FDA = Food and Drug Administration
